Forex rates fluctuation determines whether you will make a profit or a loss. In today’s fast-paced market, staying updated is essential. It’s even more important to know what drives currency fluctuations and more important the key factors that affect exchange rates. This is key to making a profit.
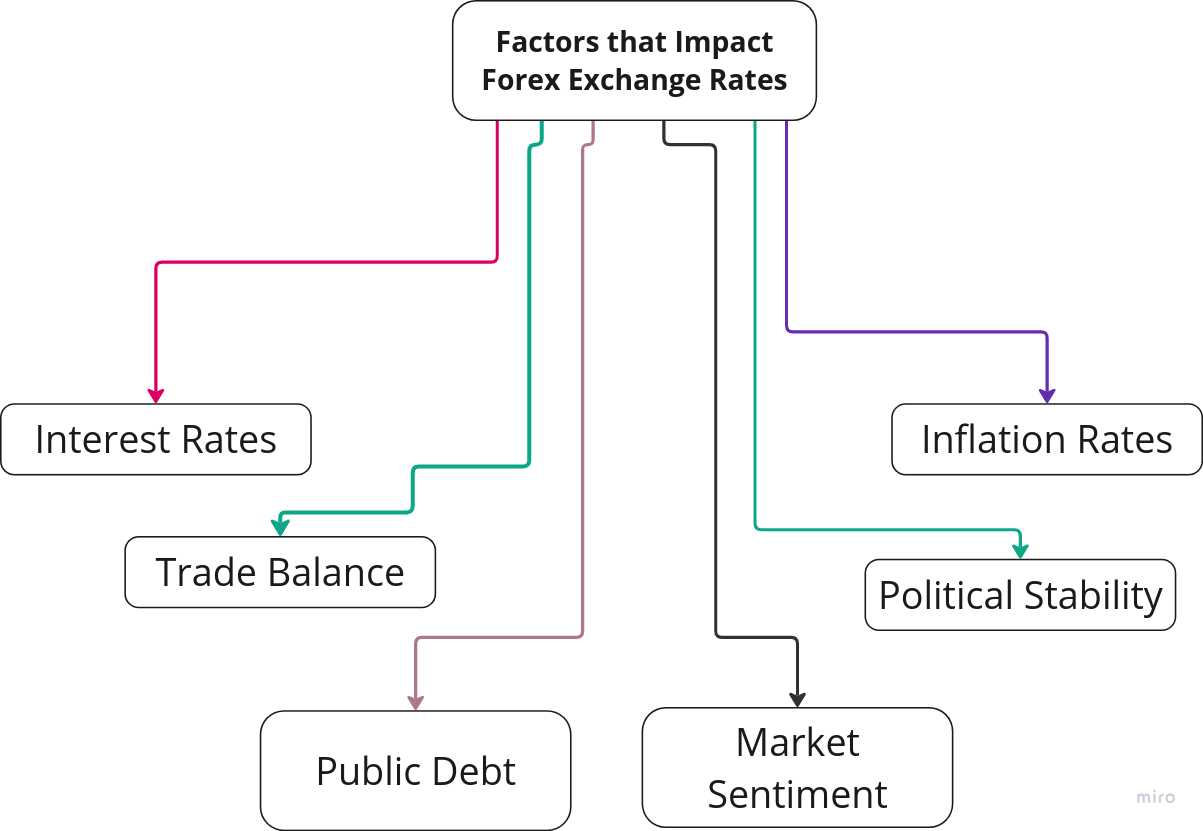
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by a central bank are one of the most significant drivers of currency value.
For example, in August 2018, the Bank of England raised interest rates from 0.5% to 0.75%. Investors then sought better returns. This caused a temporary rise in the British pound (GBP) against the US dollar (USD).(Equifax).
But, the truth is, interest rates and currency values are not one-to-one linked. If a country has high inflation, raising interest rates may weaken the currency rather than strengthen it since the actual returns on investments go down due to high inflation.
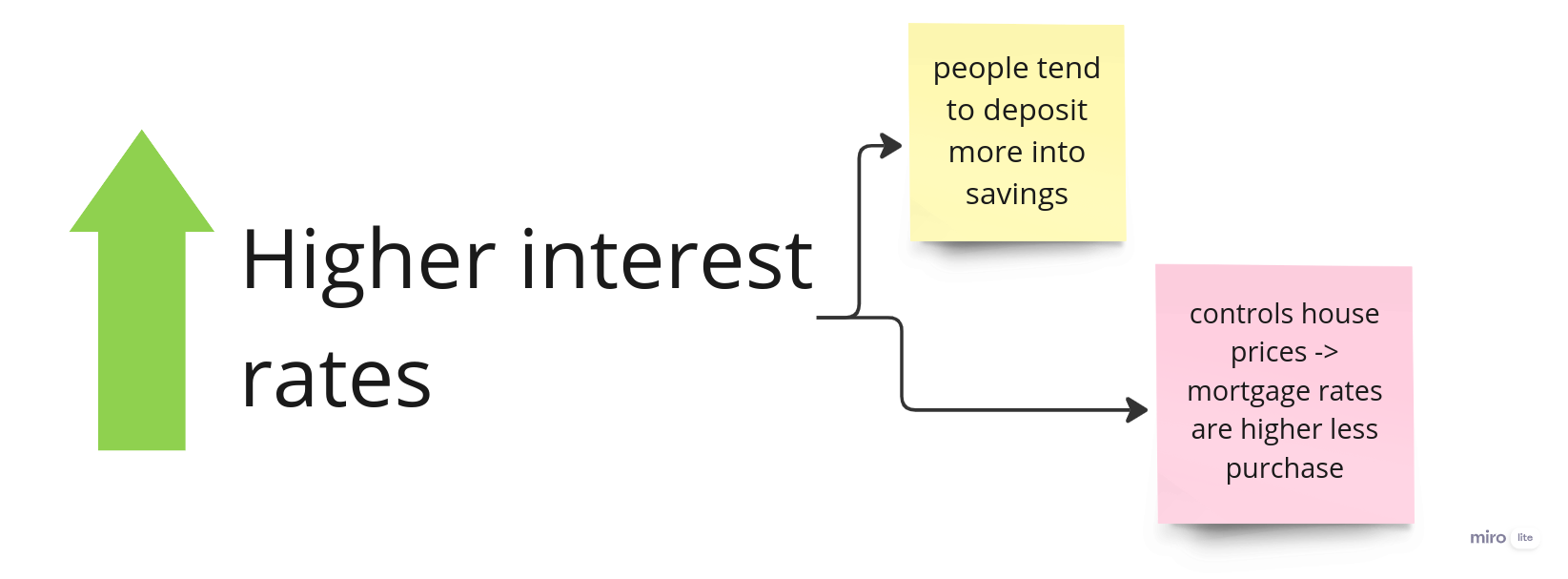
Increasing interest rate is also a technique to maintain or lower the inflation rate. It attracts people to deposit money into savings accounts. Ideally, they want fixed-term accounts that offer higher interest rates. This means more money for the bank to invest.
Inflation Rates
In forex markets, inflation significantly influences country’s currency value.
UK inflation recently rose to 2.2%, which is higher than before but still below the high of the the 2022 and 2023 cost-of-living crisis.
– High inflation weakens the GBP by reducing its value and investor confidence, making it less strong compared to currencies like the USD.
– In the early 2010s Japan faced the longest deflation with interest rates also very close to zero. The yen weakened as the Bank of Japan implemented strong monetary policy, such as printing new money (quantitative easing) in an attempt to fix their own economy.
Political Stability
Political stability boosts confidence that a country is open to foreign investors and assurance to its citizens they can rely on the bank. It is one of the main factors that affect foreign exchange rates (FX rates).
In a country that is heavily influenced by unstable politics creates an uncertainty for foreign investments and even from inside. Thus makes it risky.
Political example’s impact on currency
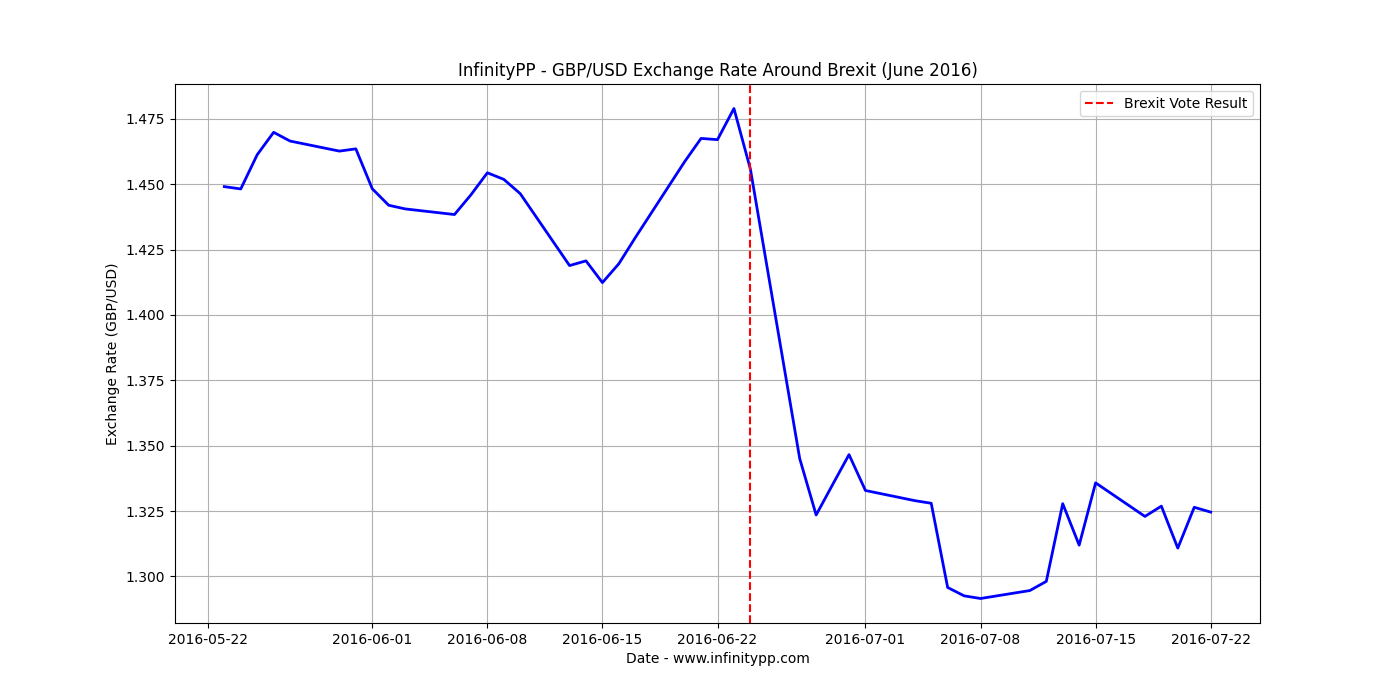
Brexit is a clear example on how fast a currency value can drop. On June 2016, sterling dropped to 31-year low due to Brexit vote. Such events in politics can have drastic impact on any currency. Imagine how difficult it will be to trade when a countries politic is un
 Similarly, political events like elections, policy changes, or geopolitical tensions can cause significant volatility in forex markets.
Similarly, political events like elections, policy changes, or geopolitical tensions can cause significant volatility in forex markets.
Sudden political events are unpredictable. So, always use a stop-loss when trading Forex on your positions to protect your money from unexpected shocks. There can be a sudden huge movements in forex pips when a pair is impacted by political events.
Trade Balance
Trade balance is the difference between a country’s exports and imports.
There are two key definitions that we need to understand:
1] Trade Surplus: When a country exports more than it imports, this results in an increase in value of the currency
2] Trade Deficit: When the import is higher than the exports it causes a drop in the value of the currency.
High demand of other foreign currencies to pay for the extra imports at a time when more was brought into Britain than sent out, drove down the pound (Office for National Statistics).
Trade balance issues are also evident in countries like the United States, where persistent trade deficits have occasionally led to a weaker USD, especially when coupled with other economic concerns.
Public Debt
A large amount of public debt can lead to inflation, and subsequently, a decrease in the currency’s value.
If a country has high debt, investors are concerned the country might default on its debts and will not be able to repay them leading to less demand for that currency.
Similar circumstances have happened in different nations as well with high public debt, like Greece during the Eurozone crisis, where fears of default and economic instability prompted a sharp decrease in the value of the euro.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment is the mood of investors and traders. They buy or sell currencies based on their opinions.
Positive sentiment results in appreciation of the currency, and negative can cause depreciation. These sentiments are often due to the country’s economic health, political stability, and prospects and can affect exchange rates.
The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in 2020 is a good example of investor sentiment both positive and negative. When Covid-19 vacinne was introduced the market sentiment turned positive while at the beginning it was negative.
Market sentiment is also evident in how traders react to upcoming events. For instance, before the 2016 Brexit referendum, a lot of traders were selling GBP in anticipation for the economic turbulence to come and value went down even further. It is the way that market sentiment can amplify the effects of other economic forces which make it an important factor in determining currency value.
In short:
Interest rates, inflation, political stability, trade balance, public debt, and market sentiment are categories that influence the level of demand for currencies so understanding these make forex trading easier. Not only are these elements recognized by the IMF, but also they can be illustrated in historical fact and real-world examples that demonstrate how influential those factors affect currency valuation. By focusing on these elements you can gain a deeper appreciation for how and why currencies fluctuate.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day. Factors can influence or change the direct of a position anytime but with planning and in-dept research before opening position helps you in becoming a better trade.